Morse Code Cipher
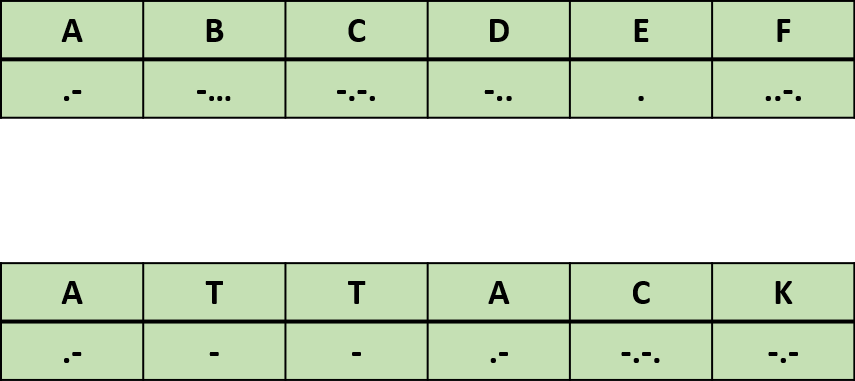
Morse code was created in 1832 by Samuel Morse as a method of communicating over long distances. It is a substitution cipher, so each Morse code symbol is mapped to a text character using a combination of “dots” and or “dashes”. To reduce the duration of transmissions, the length of each Morse character is inverse to the frequency of occurrence in the English language. For example, the letter used most frequently is “E”, so the Morse code representation is “.”, whereas the least used letter “Z” in Morse code is “--..”.
It could be easily understood by a trained listener without the use of special equipment making it a very popular form of communication in not only war applications but also in communication between civilians.
Try it out!
Additional information
For more information about Morse Code check out this YouTube video: